The Gorgeous Transformation Of Mobile Phone Chargers: A Journey Of Craftsmanship From Raw Materials To Finished Products
Raw material selection and procurement
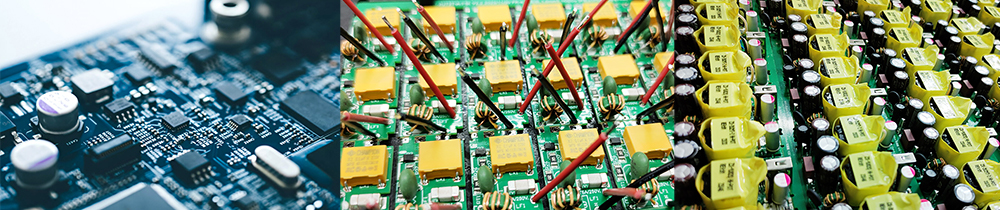
The raw materials of mobile phone chargers are varied. Manufacturers usually need to purchase the following key raw materials:
Plastic shell: The charger shell is usually made of high-quality ABS or PC plastic, which is durable and can effectively protect the internal circuit.
Circuit board (PCB): PCB is the "brain" of the charger, which carries various electronic components such as capacitors, resistors, inductors, etc. It is used to connect batteries, plugs and other electronic components.
Capacitors, resistors, inductors and other components: responsible for the stable control of current and voltage to ensure the safety and efficiency of the charger when working.
Transformer and power chip: responsible for converting the input voltage into the required output voltage and current.
USB interface, plug: interface for connecting to the device, common ones are USB-A, USB-C and Lightning interface.
Heat dissipation material: efficient heat dissipation is essential for the normal operation of the charger, especially in high-power chargers, materials such as aluminum alloy are often used to accelerate the dissipation of heat.
Design and prototyping
After selecting the raw materials, the manufacturer will carry out product design. The design process includes the appearance design, circuit design and functional planning of the charger. The design team will take the following factors into consideration:
Appearance design: The appearance of the charger needs to meet the aesthetic requirements of consumers and be easy to carry. Designers usually use CAD software for 3D modeling to ensure the size of the shell and the position of the interface are accurate.
Circuit design: The circuit design of the charger involves voltage, current and power conversion. Circuit engineers design circuits according to the specifications of power chips and components to ensure the stability and efficiency of the charger.
After the preliminary design is completed, the manufacturer will make prototype samples for testing. The testing process includes electrical performance testing, heat testing, overload protection testing, etc. to ensure the feasibility of the design.

Electronic component assembly and circuit welding
The circuit board is the core part, and various electronic components are usually mounted on the circuit board by welding.
SMT: Use an automatic SMT machine to accurately place components such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors on the circuit board.
Soldering: Use wave soldering or reflow soldering technology to firmly solder components to the circuit board. After soldering, "visual inspection" and X-ray inspection will be carried out to ensure the quality of soldering.
Testing: After the circuit board is assembled, electrical performance testing is required. Test items include voltage, current, stability, power output, etc.
Shell molding and assembly
The shell of the mobile phone charger is usually made by injection molding. This process includes the following steps:
Injection molding: Plastic particles are heated and injected into the mold, and the shell is formed after cooling. These shells may be polished, painted, and silk-screened to make them more textured.
Interface installation: Install the USB interface and plug to the shell. The plug is usually fixed to the shell by heat pressing, welding or screws.
Overall assembly: Assemble the completed circuit board and shell, and the circuit board is fixed to the interface inside the shell through connecting wires and plugs.

Functional and safety testing
The assembled charger must pass strict functional and safety tests. These tests can be divided into the following categories:
Charging performance test: Test whether the voltage and current output of the charger meet the specifications to ensure that it can charge the device in a safe and efficient manner.
Heat test: When the charger is working for a long time, it is inevitable that it will heat up. The charger must be tested for heat to ensure that the charger does not overheat during operation to avoid damaging the internal components.
Overload protection test: To ensure that the charger is not damaged when the current is too high, the charger needs to be tested for overload protection.
Electrical safety test: Including electrical insulation test, electrical interference test, short circuit test, etc., to ensure the electrical safety of the charger.

Packaging and shipment
The qualified chargers will enter the packaging stage. At this stage, the charger will be placed in a plastic bag or an anti-static bag, and the matching charging cable, user manual, etc. will also be packaged together. Finally, the charger is boxed and ready for shipment.
Packaging design: The packaging must not only protect the charger, but also have an attractive appearance design. The packaging usually contains information such as brand, product model, technical parameters and safety warnings.
Shipping: The charger will be transported to various retailers, electronic markets or consumers by sea, air or land.
After-sales and quality feedback
Manufacturers usually also provide after-sales service to deal with product quality issues or user feedback, which will help improve future products.
Green manufacturing: the integration of environmental protection and technology
With the increase of environmental awareness, the manufacturing of chargers has also paid more and more attention to environmental protection. Concepts such as recycling, energy saving, and harmless treatment are widely used. Some manufacturers have also launched chargers made of renewable materials to contribute to the cause of environmental protection.
Zonsan Conclusion
The manufacturing of mobile phone chargers is a complex and delicate process. From the selection of raw materials to the testing of finished products, every link needs to be strictly controlled. With the continuous development of charging technology, the manufacturing process of mobile phone chargers is also constantly improving. Factories must not only ensure the efficiency and safety of chargers, but also pay attention to environmental protection and user experience. Through this series of precise production processes, a safe, stable and efficient charger can be obtained.