How Does The Fast Charging Protocol Work? | ZONSAN
The fast charging protocol is the "language" needed for the charger to communicate with the device to shake hands and only after the correct "conversation" can the "handshake" be successful for fast charging. Let's take a step-by-step look at how the different fast charging protocols work.
Old-fashioned fast charging protocols

A few years ago, the fast charging protocol was very simple, so simple that it was similar to a traffic signal, and kindergarten children could determine the meaning of the signal by the color. Equipment and chargers do not need to be "smart" to read the needs of both sides, whether it is the difficulty of research and development or the cost of materials are simple and cheap. The traffic light of the fast charging protocol, on the other hand, uses D+D-voltage for information transmission.
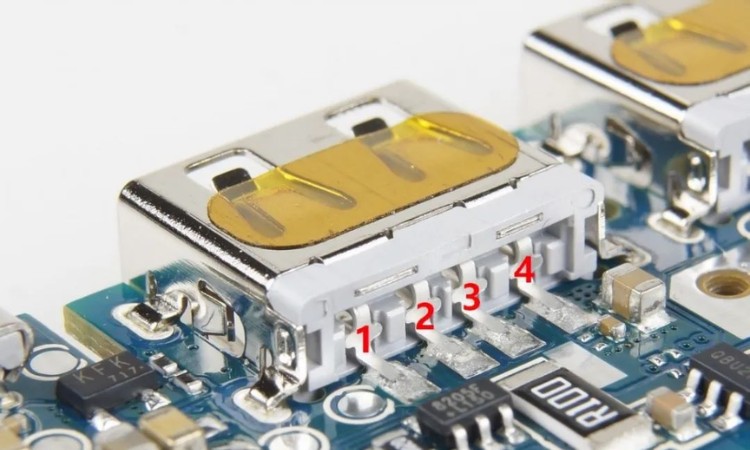

Older fast charging protocols all use the USB 2.0 communication interface, commonly found in the USB-A interface. In the picture is a USB-A output female connector on the mobile power supply, you can see that he is connected to the motherboard with only four pins, of which the two sides are used to transmit current VCC, GND pins, the middle is used to transmit data D +, D - pins. The "D" in "D+D-" stands for data data, and the charging terminal and the device receiving power communicate with each other through D+D- for data communication and thus handshake fast charging protocol.
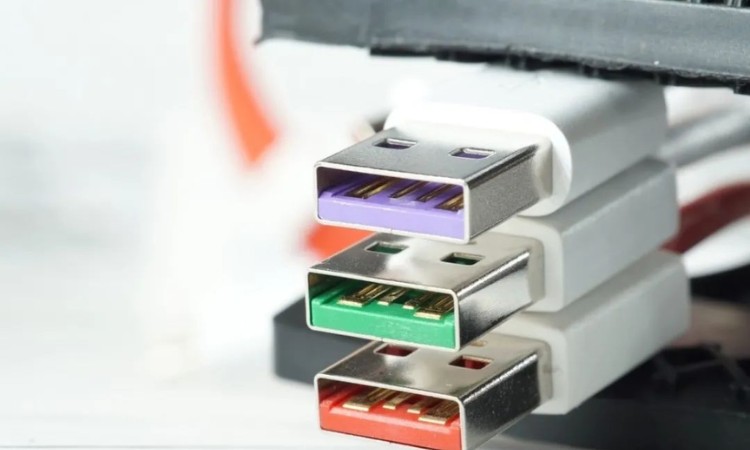

We look at the data cable, generally speaking, USB2.0 data cable USB-A interface only four contacts, and USB-A female chassis definition of the same, the two outermost is used to transfer current, the middle two is used to transfer data. vcc, GND longer, D + D- shorter, that is deliberately designed to disconnect the data connection first, after disconnecting the power supply when unplugged.
1、APPLE2.4A
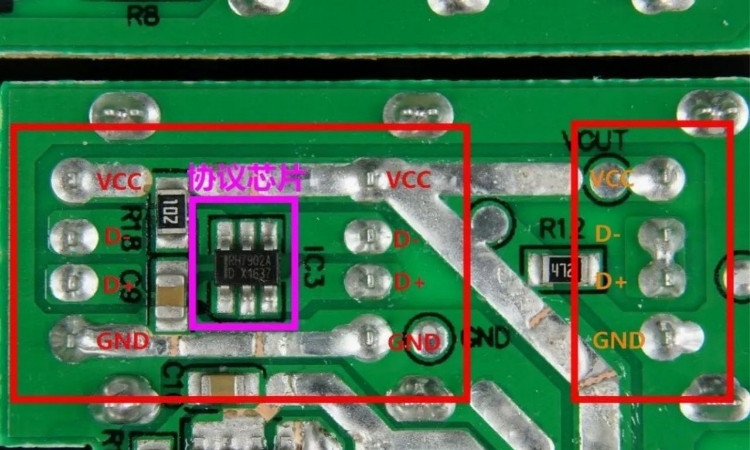
In the era of everyone is 5V charging, iPhone direct charging only 5W, the charger needs a special identification resistor to get more charging power. The left side of the PCB in the picture is the pad of the two USB-A output ports, sharing a protocol chip that supports dual intelligent identification. After the iPhone is inserted, the protocol chip adjusts the D+D- voltage of the USB-A interface to 2.7V/2.7V to provide APPLE 2.4A identification. The rightmost USB-A interface, on the other hand, simply connects D+D- directly to the short, providing DCP 5V1.5A output recognition.
Picture
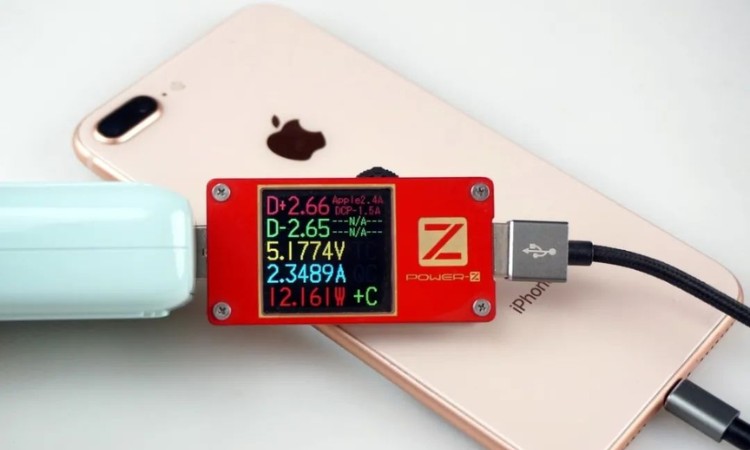

Monitoring the charging of iPhone 8 Plus through POWER-Z tester, it can be found that the current D+D- voltage is 2.66V/2.65V, which is close to 2.7V/2.7V of APPLE2.4A identification protocol. iPhone 8 Plus enters APPLE2.4A charging mode with 12W power.
2、QC2.0
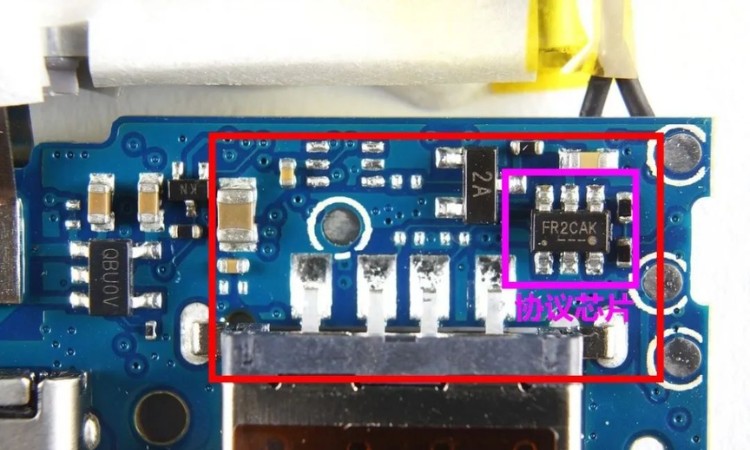
After entering the QC2.0 high-voltage fast charging era, the USB-A interface is no longer a simple 5V output, but can be boosted to 9V or even 12V voltage to obtain high-power power transmission, which there is a certain danger, what is the case before the need to boost without burning the device? So the QC era intelligent identification chip made a greater evolution, including a variety of different fast charging protocols, QC, FCP, AFC and so on, the same by controlling the D + D- voltage to polling judgment. For example, QC2.0 fast charging need to output 9V, D + D - voltage is 3.3V / 0.5V, need to output 12V, D + D - voltage is adjusted to 0.5V / 0.5V, no feedback will not be boosted to maintain 5V output to ensure safety.
3、MTK PE
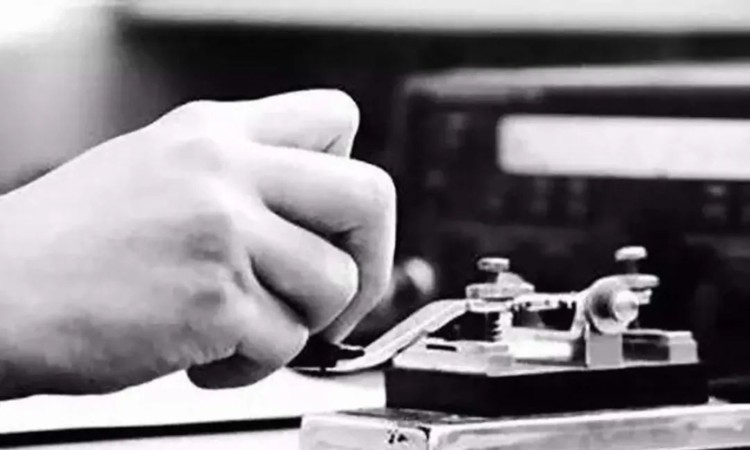

If QC2.0 based on D + D- voltage for communication is similar to a traffic light, the MTK PE fast charging used by Meizu cell phones is similar to the Morse code for telegraphing, tee - tee - tee - tee - tee -PE fast charging does not require D+D- data transfer, even only VCC GND two-core data cable can be used successfully. Two-core data cable can be successfully used and trigger PE fast charging, and the current pulse signal of PE is nearly lossless digital transmission, there will be no voltage value error that can't trigger fast charging like D+D-.
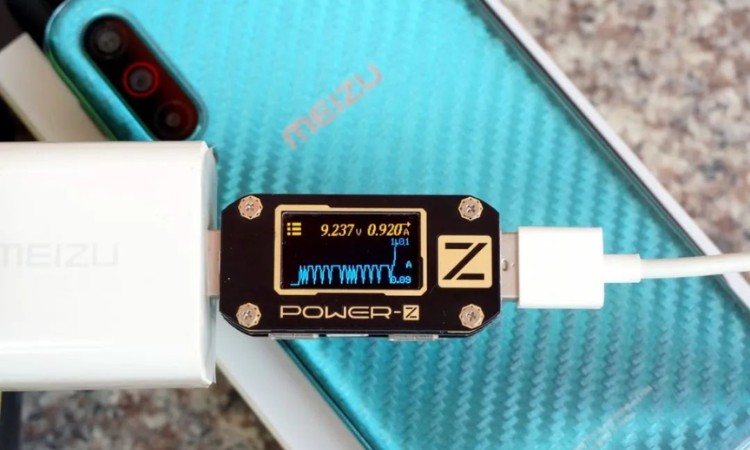

The picture shows the current pulse when POWER-Z USB tester catches Meizu triggering PE fast charging, you can see that the current on/off and interval is like telegraphing information transfer, after the correct information transfer handshake, the charger output voltage jumps from 5V to 7V and then to 9V. No longer support PE fast charging, which is beside the point.
USB PD advanced communication protocol
After entering the era of USB PD fast charging, the physical interface of the charger and digital products from the USB-A port fully transitioned to the USB-C interface, USB-C interface has more Pin pins, supports higher power transmission ceiling, and is completely different from the previous simple D + D- identification, but the means of intelligent packet two-way communication for more complex communications. If the old fast charging protocol is kindergarten students watching traffic lights to cross the road, then the USB PD fast charging protocol is two adults chatting in WeChat this level of complexity.
Let's first look at the difference between the interface, USB-C physical interface full pin form up to 24 pins, but for charging no matter how high power, are as long as the USB2.0 form of 12 pins is enough, full pin more pins are used to run USB3.0/3.1/3.2/ Thunderbolt and other high-speed data, not related to charging, the following we focus on USB2.0 standard pin USB-C interface.
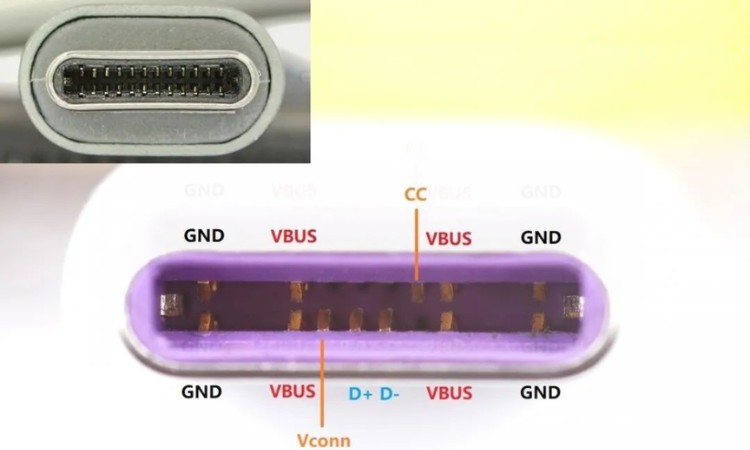
You can see the USB-C for power transmission VBUS, GND a total of two pairs that is, four pins, in addition to support front and back blind plugging, more than double the number of pins so that he can support more high-power power transmission. In the middle of the interface can be seen D + D- these two pins on the USB-A standard, so USB-C can be backward compatible data communication. And the most critical USB PD is the CC pin, CC line is the USB PD fast charging standard for information exchange channel, no CC pin then you can not PD fast charging. Some magic USB-A port, although the form is A-port, but the middle of a new pin CC line, so you can run USB PD protocol on the A-port.
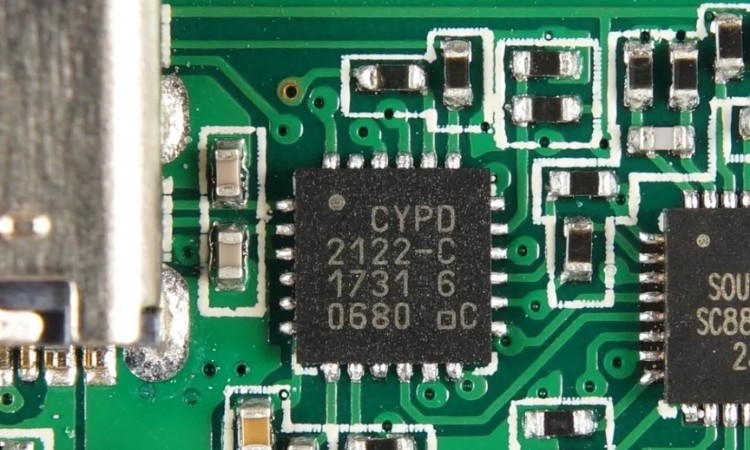

USB-C communication uses a programmable language for bi-directional communication, which requires a high-performance USB PD controller with a chip size, number of pins, and complexity that far exceeds the protocol chips of the QC era. Here we grab the communication packet between the charger and the phone via POWER-Z USB tester to see what happens during the charging process.
1. PD2.0
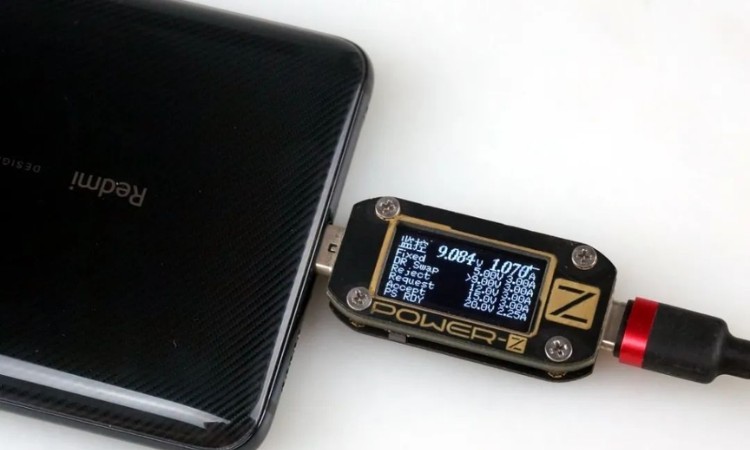

USB PD fast charging standard has now developed to PD 3.0, the larger the number the more features supported by the version, let's look at PD2.0. PD2.0 fast charging support fixed voltage gear switching, you can choose the required fixed voltage according to the charger broadcast. The voltage step for charging.
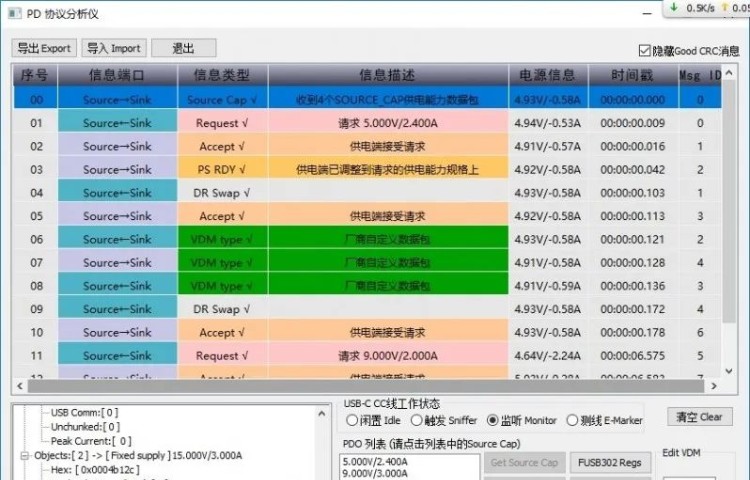
Let's take a look through the APP of POWER-Z PC, the information port column is two directions of transmission, Source->Sink, Source<-Sink, where Source->Sink represents the communication from the transmitting end to the receiving end. Source->Sink is the communication from the transmitter to the receiver, such as the charger to the phone, Source<-Sink is the feedback from the receiver to the transmitter, such as the phone to the charger, understand the direction that we can then see how they communicate with each other.
USB PD communication process we take PD 2.0 charger as an example, after the cable is plugged in the power supply and the device does not immediately start charging, but first greeting, the charger to broadcast PDO voltage, the charger told the phone, I support 5V2.4A / 9V3A / 15V3A / 20V2.25A four fixed voltage output.
After the phone receives the PDO broadcast information, it first feeds back to the charger, informing it needs 5V2.4A voltage grade, the charger receives the feedback and replies to the phone that the power has been adjusted to 5V2.4A. After that, the phone and charger communicate with each other again, the phone requests to adjust the output voltage to 9V2A, the charger informs that the request has been received and is being adjusted to 9V2A, thus completing a communication phase.
2、PD 3.0 PPS
PD3.0 PPS is close to the principle of PD2.0, but with more PPS voltage subset. PPS voltage subset is a set of power supply voltage set with 0.02V span as the adjustment range, which can fine-tune the voltage and make the charge pump fast charging and direct charging possible.
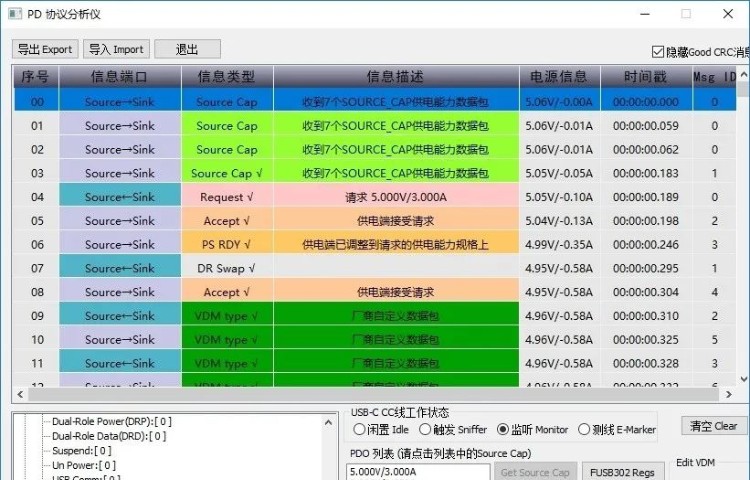
After the PD 3.0 PPS is plugged into the cable, the charger sends a packet (PDO broadcast) to the phone telling it that I am a charger with four fixed PDO's of 5V3A / 9V3A / 12V3A / 15V3A / 20V2.25A with two PPS sets of 5-11V3A / 5-16V3A. The phone receives this broadcast and gives feedback to the charger requesting output 5V3A voltage. The charger accepts the voltage adjustment request and informs the phone that it has been adjusted OK, and the phone feeds back that it is ready to charge and starts 5V3A for charging.
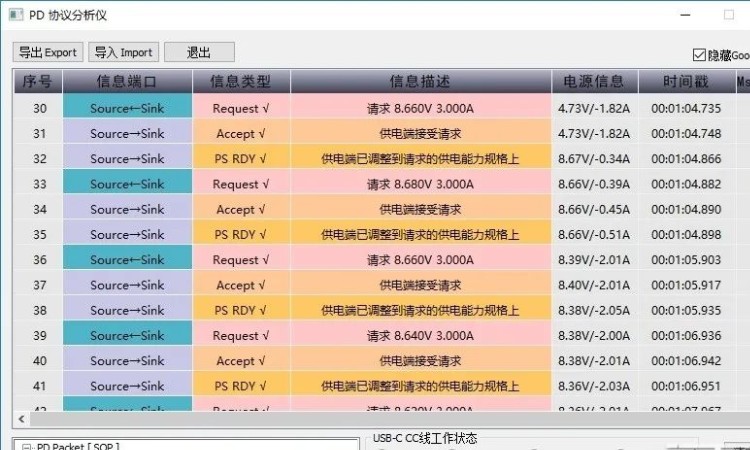
On the way to charging, the phone sends a message to inform the charger that I need to adjust the voltage and request to adjust the output voltage to 8.66V3A. The charger receives the voltage adjustment request and adjusts the output from 5V3A to 8.66V3A. After that, the phone sends the voltage adjustment command several times per second, each time telling the charger to adjust the voltage down by 0.02V, and the charger does so.
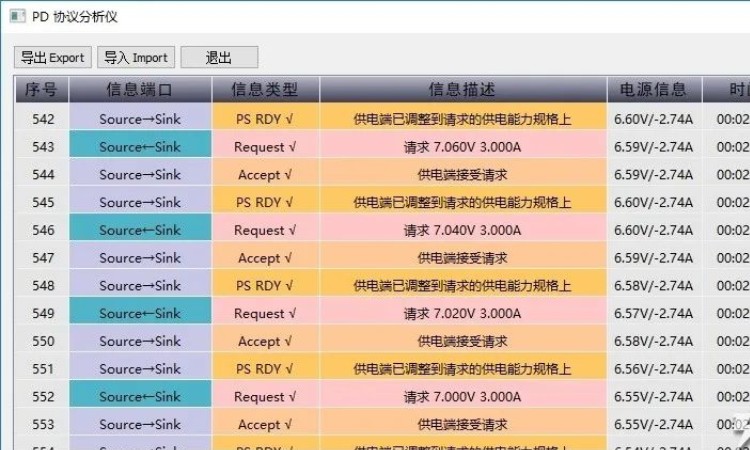
After more than 500 communications to fine-tune the voltage, it finally stabilized at 7V3A for charging, in order to achieve the purpose of fast charging and low temperature rise, which is the communication process of PPS fast charging protocol.
Private protocols
1、All-private protocols
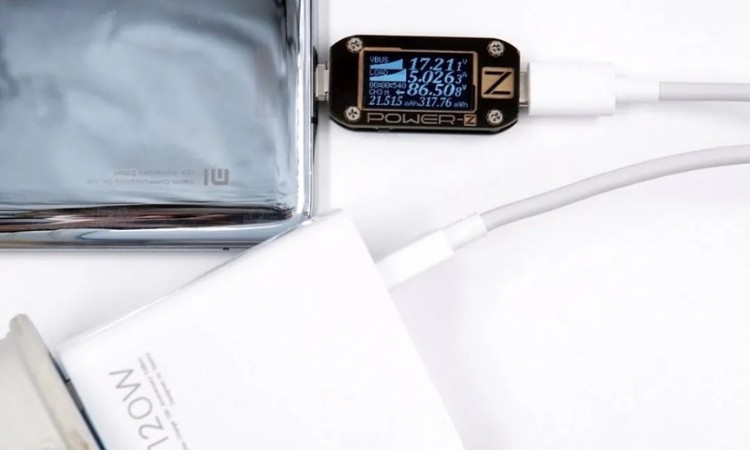

Some manufacturers will develop private fast charging protocols for some devices, encrypting the flow of information in the communication process, users want to get the best charging experience can only use the original accessories. This practice is because the current standard can not meet the needs of manufacturers, such as the USB PD limit of only 20V5A 100W, the second can build a private accessories ecosystem, enough profit to support the development of technology to achieve benign development, there is no excuse for doing so.
2、Semi-private agreement
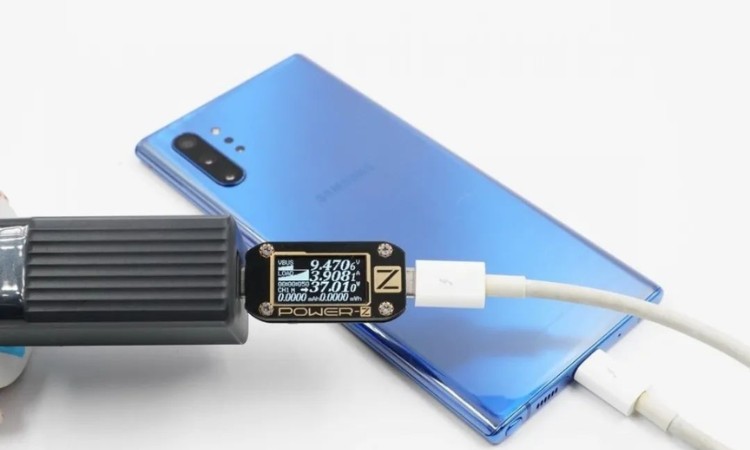

Some manufacturers are using semi-private protocols, such as Samsung 45W AFC fast charging, based on PD3.0 PPS development of fast charging protocols for fine-tuning modifications, because there is no encryption, so some of the third-party accessories on the market can also be common, the user can choose a larger range of accessories.
The benefits of unifying the USB-C interface for fast charging?

Many years ago, when the interface was not unified, there were Micro USB, Mini USB, shaped pin, DC round port and many other different interfaces, even the power supply voltage differences, chaotic chaos hindered the development of the USB-C is like a light bulb card holder, eliminating other interfaces large unified for the USB-C interface standard, so that thousands of devices are operating under the same standard, the same physical interface, the same communication standard. Manufacturers no longer need to develop technology for a variety of standards and design different specifications products, fast charging technology has been developed rapidly, users as consumers are also enjoying the convenience of USB-C unification.

USB-C is a light bulb mount, then, the charger is like a light bulb, based on the USB-C standard and the manufacture of chargers born 18W, 30W, 45W, 65W, 100W and more high-powered in the future, users can choose different power products to use according to their needs, without worrying about the interface.
Summary
This issue of charging miscellany of the editorial for you to introduce part of the fast charging protocols and principles of work, I believe that after reading you will understand. For cell phones, laptops and other devices, fast charging protocols are essential, no fast charging protocols to support the charging power will be limited to very low power, thanks to the USB-C unified standard to make fast charging fully popular, whether it is entry-level models or flagship products support fast charging, different consumer layer users can enjoy the fun of fast charging.
OEM Fast Charger Recommendation

Read More

Read More

Read More

Read More